Orthodontic Iatrogenic Damage To The Periodontium
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
if you are intersted in this article please follow for more readings
https://myorthodonticsblogg.blogspot.com/ 👈🏻
1. Periodontal disease and orthodontic treatment :
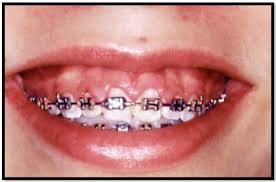
Periodontal disease includes gingivitis, alveolar bone loss (periodontitis), and loss of attached gingival support.
The periodontal reaction toward orthodontic appliances depends on multiple
factors, such as:
- Host resistance
- The presence of systemic conditions
- The amount and composition of dental plaque.
- Lifestyle factors, including smoking, can also compromise periodontal support and the negative effects of uncontrolled diabetes on periodontal support.
Bacteria present in dental plaque are the primary causative agent of periodontal disease .
Orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances is known to induce an increase in the volume of dental plaque. However, fixed orthodontic appliances cause a shift in the type of bacteria .
Therefore, fixed orthodontic treatment may result in localized gingivitis, which rarely progresses to periodontitis.
Orthodontic treatment of patients with active periodontal disease is contraindicated as the risk for further periodontal breakdown is markedly increased (Zachrisson and Alnaes, 1973; Cardaropoli and Gaveglio, 2007)
Complete evaluation of the periodontal status, especially in adult patients, is required and control of the periodontal status is necessary prior to initiation of orthodontic treatment.
Careful examination of the level of attached gingival prior to comprehensive orthodontic treatment is necessary.
The level of attached gingival is measured from the free gingival margin to the mucogingival junction minus the depth of the gingival sulcus.
Dental movement in the labio-lingual direction can be performed within the envelope of the periodontium without harmful effects on the level of attached gingiva.
If an inadequate level of attached gingiva is present prior to orthodontic treatment, a periodontic consultation should be performed, especially if labial movement of the teeth is anticipated.
Some adults develop black triangular spaces between anterior teeth. Open gingival embrasures could occur as a complication in about one third of all adult patients due to the gingival and papillary recession as a process of aging.
It should be discussed with patients before initiating ortho treatment since this may pose esthetics concerns to the patient after removal of appliances.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment